What is Polysulfone?
Polysulfone (abbreviated as PSU or PSF) is a class of high-performance thermoplastics characterized by alternating aryl and sulfonyl functional groups in their polymer structure. These materials are synthesized through polycondensation reactions between bisphenol-A and dichlorodiphenyl sulfone monomers, both derived from petrochemical feedstocks. The distinctive diphenyl sulfonyl units contribute exceptional chemical stability due to their high bond dissociation energy, which lead to superior mechanical strength and notable resistance to oxidative degradation. To optimize the material's physical properties, reinforcement strategies involving glass or carbon fiber additives are commonly employed, enabling enhanced structural performance in demanding applications.
Polysulfones are categorized as high-performance thermoplastics owing to their exceptional thermal and chemical stability. These materials exhibit a glass transition temperature (Tg) ranging from 190°C to 240°C and a heat deflection temperature (HDT) surpassing 150°C, enabling consistent performance in high-temperature environments. Their amorphous molecular structure contributes to semi-transparency and low optical distortion, while their rigid backbone minimizes creep deformation under prolonged mechanical stress. Additionally, polysulfones act as excellent electrical insulators and demonstrate inherent flame retardancy, self-extinguishing without requiring additives.
A defining feature of polysulfones is their robust chemical resistance, attributed to the diphenyl sulfonyl moiety in their molecular structure. This group provides exceptional stability against oxidation and aggressive chemicals, as the sulfone’s electron-withdrawing nature and resonance stabilization shield the polymer backbone from degradation. The delocalized electrons within the sulfone group create a stable aromatic system, resisting attacks from acids, bases, and polar solvents.
The most common types of polysulfone are:
● Polymer of Bisphenol A (PSU)
● Polyether sulfone (PES)
● Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)
These variants of polysulfone differ slightly in their molecular structure, resulting in varying degrees of heat resistance and mechanical strength.
Properties of Polysulfone
Polysulfone is known for a combination of physical and chemical properties that make it a versatile material for a wide range of applications:
● High Thermal Stability: Polysulfone has excellent heat resistance, with the ability to retain its mechanical properties even at temperatures up to 180°C (356°F). This makes it ideal for high-temperature environments where other plastics might fail.
● Chemical Resistance: It is highly resistant to a variety of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This resistance allows it to perform well in harsh chemical environments, making it popular in industries like automotive, medical, and water filtration.
● Mechanical Strength: Polysulfone exhibits impressive tensile strength and impact resistance, ensuring durability and long-lasting performance even under mechanical stress. It can withstand high loads without cracking or deforming.
● Dimensional Stability: The material has minimal shrinkage during cooling and processing, which helps maintain its shape and size, ensuring high precision in molded parts.
● Transparency: Polysulfone is naturally transparent, which allows it to be used in applications where visual clarity is required, such as in medical devices or filtration systems.
● Electrical Insulation: Polysulfone also serves as an excellent electrical insulator, making it a suitable material for electrical and electronic applications.
● Lightweight: Despite its robust mechanical properties, polysulfone is relatively lightweight, which is advantageous in applications where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Production of Polysulfone
The synthesis of polysulfone typically involves the polymerization of monomers that contain sulfone groups. The most common method is the reaction between bisphenol A (BPA) and sulfonating agents such as sodium bisulfite. The polymerization process can be carried out in a high-temperature solvent, and the resulting polymer is then extruded into pellets or molded into various forms.
Polysulfone can be produced in various forms, including sheets, films, rods, and tubes, depending on the needs of the application. These materials can then undergo further processing, such as machining, injection molding, or extrusion, to create the desired finished products.
Applications of Polysulfone
The combination of high heat resistance, chemical stability, and strength makes polysulfone a valuable material across many industries. Here are some key applications:
● Medical Devices: Due to its transparency, biocompatibility, and chemical resistance, polysulfone is commonly used in the manufacture of medical devices, such as surgical instruments, sterilization containers, and diagnostic equipment. It is also used in the production of blood filtration devices, where its ability to resist degradation from harsh sterilization processes is critical.
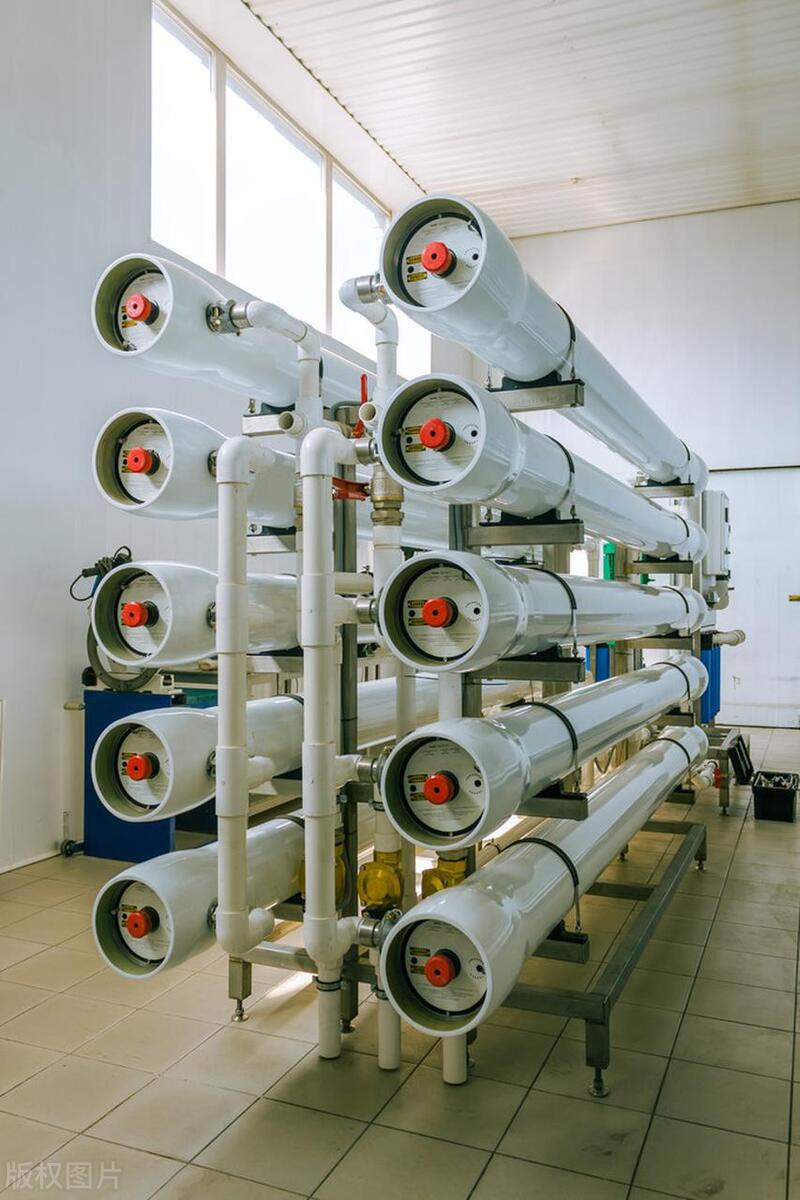
● Water Filtration: Polysulfone membranes are widely used in water filtration and purification systems, including reverse osmosis filters, because of their resistance to fouling and high chemical stability in water treatments. These membranes can effectively remove contaminants without compromising the integrity of the material.
● Automotive Industry: Polysulfone's excellent mechanical properties and high-temperature resistance make it suitable for automotive parts that need to endure extreme conditions. It is often used for parts like fuel system components, connectors, and heat shields.
● Aerospace and Defense: The lightweight and high-strength properties of polysulfone make it a popular choice in aerospace and defense applications. It is used in various components, such as aircraft interior parts, electrical enclosures, and structural components.
● Electrical and Electronic Components: Polysulfone is an excellent electrical insulator, making it ideal for use in electrical and electronic components. It is commonly used for circuit boards, connectors, and switch housings due to its resistance to heat and electrical conductivity.
● Food and Beverage Industry: Due to its chemical resistance and non-toxic nature, polysulfone is also used in the production of food and beverage processing equipment, such as filtering systems and machinery parts that come into contact with food.
● Consumer Goods: Polysulfone is employed in a variety of consumer products, including dishwasher-safe kitchenware, where high heat resistance and durability are essential.
Advantages of Polysulfone
● Versatility: Polysulfone is versatile and can be tailored for specific applications through processing and alloying with other materials.
● Durability: It provides long-term performance in demanding environments, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
● Environmental Resistance: The material withstands exposure to UV rays, extreme weather, and harsh chemicals without significant degradation.
Disadvantages of Polysulfone
● Cost: Polysulfone can be relatively expensive compared to other engineering plastics, which can be a limiting factor for some applications.
● Processing Difficulty: Due to its high melting point, polysulfone can be challenging to process and mold, requiring specialized equipment.
Conclusion
Polysulfone plastic is a highly durable, versatile, and chemically resistant material that has earned a strong reputation in various industries. Its exceptional thermal stability, strength, and dimensional stability make it an ideal choice for demanding applications such as medical devices, water filtration, automotive parts, and aerospace components. While it can be more costly and difficult to process compared to other plastics, the unique properties of polysulfone make it a material of choice for industries that require reliability and performance under extreme conditions.